KFloppy: Difference between revisions
(Feature outline) |
(Marked this version for translation) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<languages /> | |||
<translate> | |||
<!--T:7--> | |||
A Graphical Tool for formatting floppy disks | |||
[[Image:Kfloppy2.png|thumb|250px|center]] | |||
==Features== | ==Features== <!--T:2--> | ||
<!--T:3--> | |||
* Quick or full format | * Quick or full format | ||
* Bad sector checking (via Verify Integrity) | * Bad sector checking (via Verify Integrity) | ||
* Can label disk | * Can label disk | ||
* Supports command line options | * Supports command line options | ||
* Supports DOS, ext2 | * Supports DOS, ext2, UFS and Minix file systems | ||
==Usage== <!--T:4--> | |||
{{Note|A floppy cannot be formatted if it is mounted.}} | |||
<!--T:8--> | |||
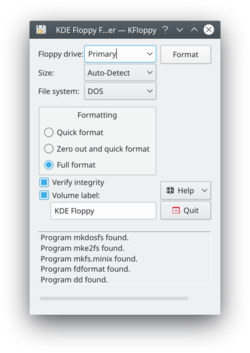
* Select the floppy drive which contains the media to be formatted | |||
<!--T:9--> | |||
* Select the size of the floppy to be used. In most cases it is safe to leave this as "Auto-Detect", and should be changed only when encountering size related issues during formatting | |||
<!--T:10--> | |||
* Select a filesystem to be used | |||
** If the desired filesystem is not listed, check the box at the bottom of the window, it may provide a reason | |||
** Not all supported filesystems are usable on floppy disks | |||
<!--T:11--> | |||
* Select the type of format to perform | |||
** Quick Format is as the name implies, the fastest process. It does check for bad blocks or other errors | |||
** Zero out and quick format will overwrite each sector with zeroes. This should not be relied on for securely erasing a disk, only a quick method of destroying data | |||
** Full format will format the media, and check for bad blocks and other filesystem defects if possible | |||
<!--T:12--> | |||
* Check '''Verify Integrity''' if KFloppy is to check if the format was successful | |||
<!--T:13--> | |||
* Provide a name for the floppy, if desired | |||
<!--T:14--> | |||
* Click '''Format''' to format the media | |||
==More Information== <!--T:5--> | |||
Read about the full capabilities in [http://docs.kde.org/development/en/kdeutils/kfloppy/index.html the application's Handbook] | |||
<!--T:6--> | |||
[[Category:Utilities]] | |||
[[Category:File Management]] | |||
</translate> | |||
Latest revision as of 06:41, 26 December 2018
A Graphical Tool for formatting floppy disks
Features
- Quick or full format
- Bad sector checking (via Verify Integrity)
- Can label disk
- Supports command line options
- Supports DOS, ext2, UFS and Minix file systems
Usage
Note
A floppy cannot be formatted if it is mounted.
- Select the floppy drive which contains the media to be formatted
- Select the size of the floppy to be used. In most cases it is safe to leave this as "Auto-Detect", and should be changed only when encountering size related issues during formatting
- Select a filesystem to be used
- If the desired filesystem is not listed, check the box at the bottom of the window, it may provide a reason
- Not all supported filesystems are usable on floppy disks
- Select the type of format to perform
- Quick Format is as the name implies, the fastest process. It does check for bad blocks or other errors
- Zero out and quick format will overwrite each sector with zeroes. This should not be relied on for securely erasing a disk, only a quick method of destroying data
- Full format will format the media, and check for bad blocks and other filesystem defects if possible
- Check Verify Integrity if KFloppy is to check if the format was successful
- Provide a name for the floppy, if desired
- Click Format to format the media
More Information
Read about the full capabilities in the application's Handbook
