Amarok/Manual/Organization/Collection/RemoteCollections/DAAP: Difference between revisions
m (add anchor) |
m (fix llevels) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<span id="Digital Audio Access Protocol (DAAP)"> | <span id="Digital Audio Access Protocol (DAAP)"> | ||
<translate> | <translate> | ||
== Digital Audio Access Protocol (DAAP) == <!--T:1--> | ===== Digital Audio Access Protocol (DAAP) ===== <!--T:1--> | ||
<!--T:2--> | <!--T:2--> | ||
DAAP is a protocol to share media over a network. It was first used for the '''iTunes''' music player, but is widely used today. | DAAP is a protocol to share media over a network. It was first used for the '''iTunes''' music player, but is widely used today. | ||
=== Client === <!--T:3--> | ===== Client ===== <!--T:3--> | ||
<!--T:4--> | <!--T:4--> | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
[[File:remotecollections_daap.png|center|350px]] | [[File:remotecollections_daap.png|center|350px]] | ||
=== Server === <!--T:6--> | ===== Server ===== <!--T:6--> | ||
<!--T:7--> | <!--T:7--> | ||
Revision as of 18:07, 5 November 2011
Digital Audio Access Protocol (DAAP)
DAAP is a protocol to share media over a network. It was first used for the iTunes music player, but is widely used today.
Client
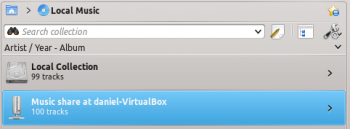
Amarok automatically shows the tracks from the server in the Media Sources -> Local Music pane and no further configuration is required. If the collection is not showing up, click the icon to be sure you are not in Merged View.
Server
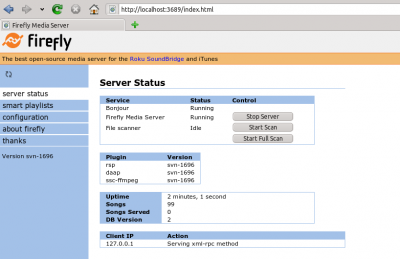
On Debian-based distributions like Ubuntu you can install a DAAP server using
sudo apt-get install mt-daapd
This will install the Firefly DAAP server. You can configure it using its web interface by opening the page
http://localhost:3689/index.html
. The default password is mt-daapd; the user field stays empty.