KWin Rules Window Matching/da: Difference between revisions
(Importing a new version from external source) |
(Importing a new version from external source) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== | == Vindue-matchning == | ||
[[Image:kwin-window-matching.png|350px|center]] | [[Image:kwin-window-matching.png|350px|center]] | ||
Revision as of 20:16, 8 March 2012
Vindue-matchning
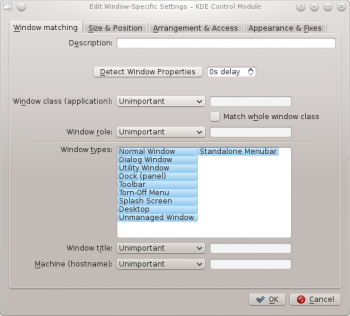
The tab is used to specify the criteria KWin uses to evaluate whether the rule is applicable for a given window.
Zero (match any window) or more of the following may be specified:
- - match the class.
- - include matching the secondary class.
- - restrict the match to the function of the window (e.g. a main window, a chat window, etc.)
- - restrict the match to the type of window: Normal Window, Dialog Window, etc.
- - restrict the match to the title of the window.
- - restrict the match to the host name associated with the window.

Tip
While it's possible to manually enter the above information, the preferred method is to use the button.
For each field, the following operators can be applied against the field value:
- - ignore the field.
Note
Both and implement case insensitive matching. For example, AB matches the string AB, ab, Ab and aB.
- - Qt's regular expressions are implemented - see pattern matching using regular expressions.
Detect Window Properties
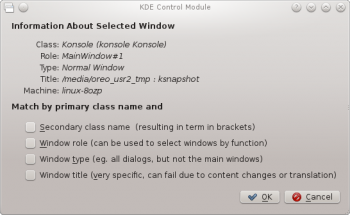
The function simplifies the process of entering the matching-criteria.
- For the application you'd like to create a rule, start the application.
- Next, in the tab, set the number of seconds of delay before the function starts. The default is zero seconds.
- Click on and
- When the mouse-cursor turns to cross-hairs, place it inside the application window (not the title bar) and left-click.
- A new window is presented with information about the selected window. Select the desired fields:
- Secondary class name - some applications have a secondary class name. This value can be used to restrict windows by this value.
- Window role
- Window type
- Window title
Click the button to back-fill the criteria.
By using a combination of the information, a rule can apply to an entire application (by Class) or a to a specific window Type within the Class - say a Toolbar.
