Kdenlive/Manual/Clip Menu/Stabilize: Difference between revisions
(update transcode doco based on conversation with the author of the original work on this Georg Martius) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
=== stabilize ( vstab) === <!--T:9--> | === stabilize ( vstab) === <!--T:9--> | ||
This is based on [http://vstab.sourceforge.net/ this] work. | |||
<!--T:4--> | <!--T:4--> | ||
Revision as of 09:52, 9 January 2013
Stabilize
This menu item is available from right click on a clip in the project tree or under the project menu when a clip is selected in the project tree.
This feature applies image stabilization algorithms to the clip which can reduce the shakiness of a shaky bit of footage.
There are two different methods of stabilization available in Kdenlive - vstab and transcode.
This video shows a side by side comparison between vstab and transcode stabilize methods.
{{#ev:youtube|86SUhodScDE}}
stabilize ( vstab)
This is based on this work.
This tutorial shows how to use the stabilize feature - vstab version:
{{#ev:youtube|SWCoqZLJNgY}}
The "shutter angle" setting that the narrator says he does not know what it does (1:35) ... Shutter angle is an angle that images could be maximum rotated for stabilization. see here.
stabilize (transcode)
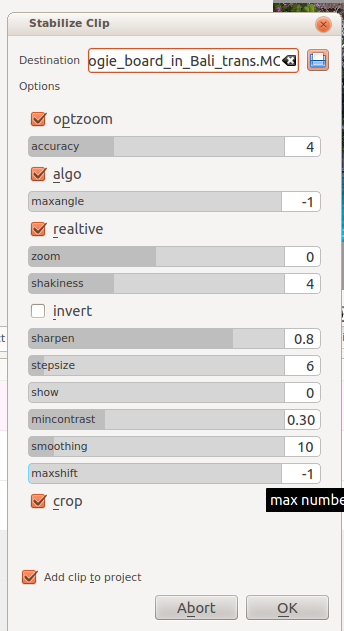
Based on the tooltips from this screen and the docs here this what all the options mean:
optzoom = use optimal zoom (calculated from transforms). Causes video to zoom until 90% of transformations are hidden. default - checked. Hint: You can further zoom in with the zoom option
accuracy = accuracy of shakiness detection. Should be >=shakiness factor. 1: low (fast processing) 15: high (slow processing) - default 4. Recommended 8
algo (= algorithm used) checked= small measurement fields - default = checked. Unchecked means use brute force algorithm. The brute force algorithm is deprecated.
maxangle = maximum angle to rotate - in radians. default = -1 which means no limit
relative unchecked = absolute transform (don't use this), checked = relative transform. Default is checked.
zoom - Additional zoom during transform. Percentage to zoom > 0 = zoom in, <0 = zoom out. The zoom specified here is additional to the optimum zoom calculated by the program when optzoom is checked. default = 0
shakiness - how shaky is the video. and how quick is the camera? 1: little (fast processing) 10: very strong/quick (slow processing) Default = 4. Note: large values may also reduce the accuracy. This is due to the internals of the movement-detection. Typically you don't need a value greater than 7.
invert - invert the transform. default = unchecked. Inverting the transform is pointless - leave unchecked.
sharpen - sharpen transformed image. amount of sharpening: 0: no sharpening. uses filter unsharp with 5x5 matrix Default = 0.8
stepsize - step size of search process, region around minimum is scanned with 1 pixel resolution- default = 6
show 0= draw nothing, 1 or 2 = show fields and transforms. Use 1 or 2 to preview what the process is going to do. example default = 0. Non-zero values of this parameter are not relevant in the Kdnlive implementation - use zero.
mincontrast below this contrast - the field is discarded. Range 0-1 default =0.3. You may want to used a smaller value for a really low contrast clip.
smoothing Controls the amount of smoothing/stabilization. The larger the value for smoothing the more camera movements are compensated. The resulting clip has a lower change in camera speed.
Technically it is the number of frames for lowpass filtering = smoothing * 2 + 1.
Eg with a with 25 fps clip, a value of 12 for the smoothing factor means we would smooth over one second - 12 frames behind the current frame + the current frame (1) + 12 frames after the current frame. default =10
Demo of the difference here (top:3, bottom: 30)
maxshift maximal number of pixels to translate image. (default = -1 no limit)
crop unchecked = The border of the transformed frames contains the pixels from previous frames. Checked = black background. default = unchecked
Example of the effect of running stabilize - transcode from the orignal author - Georg Martius
{{#ev:youtube|HYE3KAl8RAQ}}