Amarok/Manual/Organization/Collection/ExternalDatabase: Difference between revisions
(added navigation bar) |
m (adding tag) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Amarok]] | [[Category:Amarok]] | ||
{{Construction}} | |||
{{Todo|add images (get those from the original article: [http://amarok.kde.org/wiki/MySQL_Server]}} | {{Todo|add images (get those from the original article: [http://amarok.kde.org/wiki/MySQL_Server]}} | ||
Revision as of 12:25, 20 August 2010

Configuration
Amarok 2.2 and above support an external MySQL database as a backend.
MySQL Setup
On your MySQL server, run a command like:
"GRANT ALL ON amarok.* TO 'amarokuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'mypassword'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;"
Be sure to substitute for "amarokdb", "amarokuser", "localhost", and "mypassword" as appropriate.
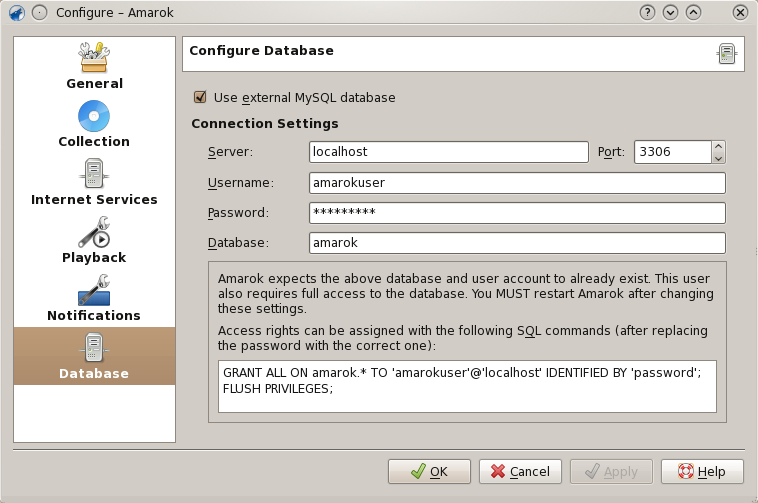
With newer versions of Amarok you can configure the database from within Amarok at Settings --> Configure Amarok --> Database. See the screenshot below.
If you have an older version, you may need to add the database via your amarokrc file, usually in ~/.kde4/share/config/amarokrc. Add a [MySQL] section:
[MySQL] UseServer=true Database=amarok Host=localhost Password=mypassword User=amarokuser
Migrating from MySQL Embedded to MySQL Server
If you want to maintain the statistics, etc. that you have in the embedded MySQL database from before Amarok 2.2, you can do the following:
First, start Amarok 2.2 at least once to give the database a chance to update to the latest schema version.
Next, kill the running MySQL service
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql stop
and start a MySQL daemon from your ~/.kde4/share/apps/amarok directory (--defaults-file MUST be the first option!):
/usr/sbin/mysqld --defaults-file=`pwd`/my.cnf --default-storage-engine=MyISAM --datadir=`pwd`/mysqle --socket=`pwd`/sock --skip-grant-tables
The skip-grant-tables means you can use any password or username to connect to it. 'localhost' will not work, the MySQL client will try to use a unix socket. Using 127.0.0.1 as the host makes it work. Some systems may restrict this access through apparmor or SELinux. They can be temporarily disabled with
sudo /etc/init.d/apparmor stop
Now, run mysqldump, passing in the -S option to specify the local socket. This will dump your old embedded DB out to a SQL file.
mysqldump -S sock amarok > amarok.mysql
You can then restart your MySQL service and load this SQL file into your mysql server. You'll have needed to already run the GRANT statement above and create an amarok database ("CREATE DATABASE amarok;"):
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql stop mysql -u amarokuser -p amarok < amarok.mysql
NOTE: You may need to re-scan your collection in Amarok after completing this.