Showfoto/White Balance/uk: Difference between revisions
Created page with 'Давайте відкриємо фотографію у '''Showfoto''' і скористаємося пунктом меню <menuchoice>Колір -> Баланс білог...' |
Created page with 'Буде відкрито панель, подібну до такої:' |
||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
|} | |} | ||
Буде відкрито панель, подібну до такої: | |||
{|class="tablecenter" style="border:1px solid darkgray;" | {|class="tablecenter" style="border:1px solid darkgray;" | ||
Revision as of 18:04, 22 September 2010
Посібник з обробки фотографій у KDE 1-3: Баланс білого
Unai Garro (uga) — літо 2008 року
Це третій посібник у цьому наборі, присвяченому демонстрації ефективності програм для обробки фотографій у KDE для виправлення і/або покращення ваших фотографій. У першому і другому посібниках ми виправляли вади, пов’язані з освітленням, тобто ми розглядали фотографії, на яких були занадто темні або занадто світлі ділянки. Ми розглянули способи виправлення за допомогою інструменту виправлення рівнів та інструменту виправлення кривих.
У цій третій частині ми продовжимо виправляти вади, пов’язані з освітленням, але розглядатимемо вади, пов’язані з кольорами, а не з яскравістю.
Отже, почнемо!
Здебільшого ми знімаємо на природі або на вулиці. Освітлення чудове, світить сонце, а у нас виходять чудові знімки. Але іноді доводиться знімати у приміщеннях, на вечірках або на конференціях, де умови освітлення не є найкращими. Іноді навіть доводиться знімати зі спалахом. Ви можете спитати: «У чому ж проблема?» Гаразд, іноді вплив освітлення непомітний, але приміщення освітлюються або лампами розжарювання (жовтувате або червонувате світло), або лампами денного світла (блакитне світло). Залежно від умов освітлення результати фотографування можуть бути доволі різними.
Давайте розглянемо наведений нижче приклад зі знімків конференції Akademy 2008. Знімок було люб’язно надано для цього посібника Себастьяном Кюглером (Sebastian Kügler):

|
Так, це Майк і Пол, які обговорюють проблеми зворотної сумісності змін у основних компонентах kdelibs на серйозній зустрічі Akademy!
Ой, здається, обличчя Майка дещо червонувате? Хіба це природній колір? Можливо, це наслідки бурхливої дискусії? ...Але, ні, це лише погане освітлення!
So what happenned to that photo. Simply, the room was poorly illuminated by yellowish tungsten lamps, and the camera captured that nicely. Our eyes (or rather, our brain), compensate it automatically to identify the colors, but cameras not always manage doing that.
Most or all digital cameras these days allow correcting that when taking the picture, with an option called "white balance (WB) setting". The menu is usually similar to the following image:

|
If the camera was set like in this picture (light bulb/tungsten light selected), the picture would have turned out better colored. In the same camera menu, you will find many more options for cloudy/sunny days, fluorescent light, flash light, etc. Please refer to your own camera's manual for more details, since each particular camera is different.
By default, though, cameras are usually preset to . This means that the camera will try guessing which setting of all is the most adequate in each case. It can work nicely, but honestly, most of the times they fail while indoors, like in this case.
Що ж робити? Нам знову допоможе Showfoto!!!
Давайте відкриємо фотографію у Showfoto і скористаємося пунктом меню :

|
Буде відкрито панель, подібну до такої:

|
Звучить доволі складно, чи не так? Гаразд, це доволі просто. Найважливішими є дві верхні частини.
Обидва інструменти виконують однакові завдання, але вхідні дані для кожного з них є різними.
The second tool is what you already know. It's equivalent to the camera's . There are different presets for each light types: 40watt lamps, 100 watt lamps... You can select one of them, and it should fix the colors, but... which of them is the correct one for our light source? hard choice, huh?
The first tool is much more flexible. It allows adjusting the Kelvin Temperature of the light. The Kelvin temperature indicates just if the light source was warmer (reddish), or colder (bluish). The more you move the slider to the right, the orange/redder the image will become. The more you move it to the left, the more blueish it will turn. But this tool can be a bit hard to tweak, and usually requires extra hard work like adjusting the green color slider. Not very easy to do.
So what's the solution? It's easy. In the same dialog, right besides the Kelvin temperature setting, you will find a color picker as shown in the next picture. The color picker allows us selecting a point in the original image that should have been white or gray (i.e., not colored, same R=G=B values).
Most pictures have such places. For example, Mike's t-shirt is possibly white around his neck, given the photograph. So I clicked on it:
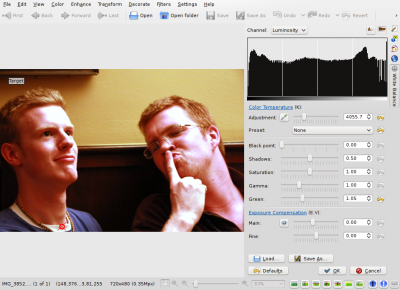
|
Impressive, isn't it? Yes, that's the power of white balance correction. Now you really get to see the real colors in the photograph. You can now know that his face isn't orange, the wall was actually painted yellow, and his t-shirt was dark blue. You can adjust further the tool manually by adjusting the Kelvin temperature, brightness of the picture etc. (for length reasons, I will leave the exploring of those tools to the reader).
I could just be satisfied with this photo and be done with the tutorial, but I am not. Look at Mike's forehead, the tool has overexposed it and it's all white now. There's no information there, we clipped the histogram. Somehow, for reasons unknown to me, Showfoto's white balance tool has a tendency to do this in some photos where highlights exist and have little detail. And no matter how much you tweak the tool you may not get it right, like in this case. But I won't give up.
If you remember from the second tutorial, we learned how to adjust the brightness of the image using curves. Lets do it then. BEFORE applying the white balance tool, lets darken a bit Mike&apss forehead:
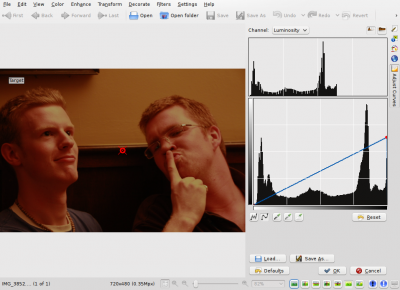
|
(Notice that moving the right point of the curves tool down is equivalent to using the levels tool, and moving the maximum output level left. Give it a thought.
And now yes, after repeating the same process, I got the forehead not that much overexposed:
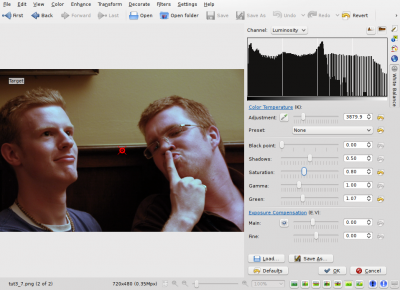
|
In the same tool, I adjusted saturation a bit lower since the shadows were still a bit reddish, and yes. Now just press .
Before presenting the image, adjust a bit levels (as shown before in the first tutorial) and we are now done:

|
Another nice photo and tool for our collection - thanks Mike and Paul for this great image and I really hope you enjoy these series. Feel free to give suggestions for improvements and cya in the next tutorial!
