Amarok/Manual/Organization/Collection/ExternalDatabase/pl: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "Połącz się z lokalną bazą danych używając {{Input|1=mysql -u root -p}} Zostaniesz poproszony o hasło użytkownika '''root''' bazy '''MySQL'''. Następnie powinieneś zoba...") |
(Created page with "===== Konfiguracja Klienta =====") |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
{{Input|1=sudo service mysql restart}} | {{Input|1=sudo service mysql restart}} | ||
===== | ===== Konfiguracja Klienta ===== | ||
Open the configuration dialog by clicking <menuchoice>Settings -> Configure Amarok... -> Database</menuchoice>. Enable the checkbox and enter the user data.<br /> | Open the configuration dialog by clicking <menuchoice>Settings -> Configure Amarok... -> Database</menuchoice>. Enable the checkbox and enter the user data.<br /> | ||
Revision as of 15:17, 29 November 2011
Zewnętrzna Baza Danych
Amarok 2,2 i powyżej oferuje wsparcie dla baz danych zewnętrznychMySQL jako backendu.
Konfiguracja Serwera
Instalacja Serwera MySQL
Najpierw musisz zainstalować serwer MySQL. Na dystrybucjach opartych o Debiana takich jak Ubuntu możesz użyć
sudo apt-get install mysql-server mysql-client
by to zrobić. Zostaniesz poproszony podczas instalacji o podanie hasła root dla bazy danych. Pakiet mysql-client wymagany jest do wykonania niektórych z poleceń w tym dokumencie, ale nie jest wymagany do używania Amarok.
===== Konfiguracja Bazy Danych
Połącz się z lokalną bazą danych używając
mysql -u root -p
Zostaniesz poproszony o hasło użytkownika root bazy MySQL. Następnie powinieneś zobaczyć znak zachęty:
mysql>
.
Stwórz nowego użytkownika amarokuser z hasłem amarokpass używając
CREATE USER 'amarokuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'amarokpass';
. Amarok potrzebuje swojej własnej bazy danych, która zostanie stworzona poleceniem
CREATE DATABASE amarokdb;
Daj użytkownikom dostęp do bazy poleceniem
GRANT ALL ON amarokdb.* TO 'amarokuser'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'amarokpass';
Znak % jest to wieloznacznik pozwalający dowolnemu hostowi na połączenie z bazą danych. Teraz użyj
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
by przeładować wewnętrzne ustawienia używane przez MySQL. W końcu
exit
zamyka linię poleceń MySQL
Standardowo serwer jest jedynie dostępny dla połączeń lokalnych. Zmienić można to w pliku /etc/mysql/mycnf i dostosować adres przy bind-address tak by odpowiadał jednemu na którym serwer ma nasłuchiwać połączeń. 0.0.0.0 nasłuchuje na wszystkich interfejsach. Po zapisaniu musisz restartować serwer używając
sudo service mysql restart
Konfiguracja Klienta
Open the configuration dialog by clicking . Enable the checkbox and enter the user data.
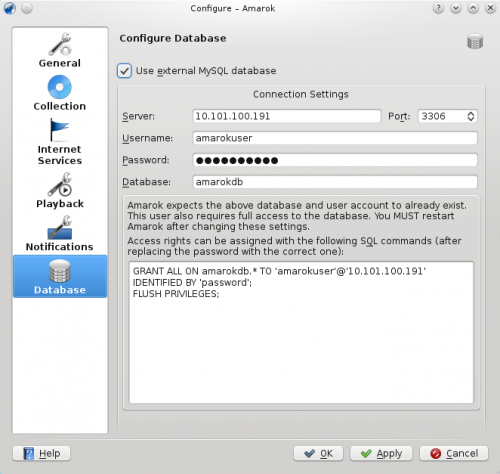
You need to restart Amarok so that the changes take effect.
Migrating from MySQL Embedded to MySQL Server
If you want to maintain the statistics, etc. that you have in the embedded MySQL database from before Amarok 2.2, you can do the following: First, start Amarok 2.2+ at least once to give the database a chance to update to the latest schema version.
Next, kill the running MySQL service
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql stop
and start a MySQL daemon from your ~/.kde4/share/apps/amarok directory (--defaults-file MUST be the first option!):
/usr/sbin/mysqld --defaults-file=`pwd`/my.cnf --default-storage-engine=MyISAM --datadir=`pwd`/mysqle --socket=`pwd`/sock --skip-grant-tables
The skip-grant-tables means you can use any password or username to connect to it. 'localhost' will not work, the MySQL client will try to use a Unix socket. Using 127.0.0.1 as the host makes it work. Some systems may restrict this access through apparmor or SELinux. They can be temporarily disabled with
sudo /etc/init.d/apparmor stop
Now, run mysqldump, passing in the -S option to specify the local socket. This will dump your old embedded DB out to a SQL file.
mysqldump -S sock amarok > amarok.mysql
You can then restart your MySQL service and load this SQL file into your MySQL server. You'll have needed to already run the GRANT statement above and create an Amarok database ("CREATE DATABASE amarok;"):
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql stop mysql -u amarokuser -p amarok < amarok.mysql
