KWin Rules: Difference between revisions
| Line 116: | Line 116: | ||
: The width and height of the window. | : The width and height of the window. | ||
;Maximized horizontally, Maximized vertically, Fullscreen | ;Maximized horizontally, Maximized vertically, Fullscreen | ||
: These attributes are used to toggle the maximum/minimum/full-screen window attribute. | : These attributes are used to toggle the maximum horizontal/minimum horizontal/full-screen window attribute. | ||
;Desktop | ;Desktop | ||
: | : Place the window on the designated ''(Virtual) Desktop'' Use '''All Desktops'' to place the window on all ''Virtual Desktops''. | ||
;Minimized | ;Minimized, Shaded | ||
: | : Toggle the Minimize and Shading window attribute. For example, a window can be started Minimized or if it is started Minimized, it can be forced to not. | ||
: {{Tip|Maximized attribute is emulated by using both '''Maximized horizontally''' and '''Maximized vertically'''.}} | |||
: | |||
;Initial placement | ;Initial placement | ||
: | : Override the global window placement strategy. | ||
;Ignore requested geometry | ;Ignore requested geometry | ||
: | : <---- placeholder ... | ||
;Minimum size | ;Minimum size | ||
: Def | : Def | ||
Revision as of 15:14, 27 February 2012
Overview
KWin allows the end-user to define rules to alter the behavior of an application's windows.

Tip
For example, when an application is started, it can be forced to always run on Virtual Desktop #2. Or a defect in an application can be worked-around by using a rule to, say, always force the window on top of all others.
This page will define the different settings and the attributes. For the impatient folks, working examples will be listed. Whenever possible, screen shots will be used to show example settings.
KWin Rule Editor
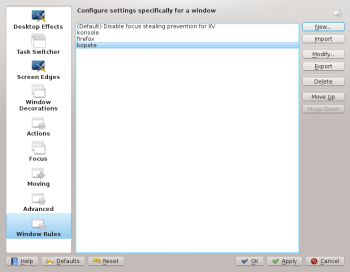
Invoking the Editor
There are several ways one can invoke the Rules editor. Below are a couple:
- Right-click on the title-bar of any window, choose and in the Configure window, select or
Anatomy
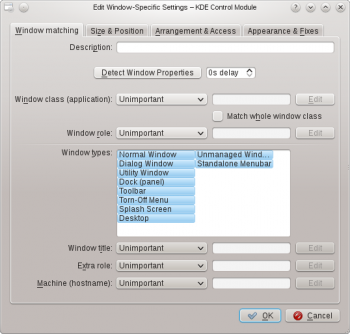
The editor is composed of four tabs:
As the name implies, is used to specify criteria to match one or more windows. The other three tabs are used to alter the characteristics of the matching windows.
Rules
Evaluation
KWin evaluates the rules when an application starts and after editing rules. Any matching rule's attribute(s) override the application's corresponding attribute(s).
Precedence
In the window, the rules are listed in the order in which they are processed.
The rule at the top of the list is processed first, followed by the next rule until the end of the list is reached.
Conflicts
In the event two rules match a window and affect the same attribute, the first rule in the list takes precedence.
Window Matching
The tab provides a series of matching-criteria fields used to identify application windows:
- - match this window and all its children windows.
- and
- - restrict the match to the function of the window (e.g. a main window, a chat window, etc.)
- - restrict the match to the type of window: Normal Window, Dialog Window, etc.
- - restrict the match to the title of the window.
- - restrict the match to the host name associated with the window.

Tip
For each field, the following operators can be applied against the field value:
- - Qt's regular expressions are implemented. For additional information, web search qt regex nokia.
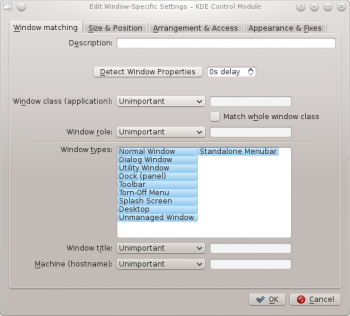
Detect Window Properties
The function simplifies the process of entering the matching-criteria.
- For the application you'd like to create a rule, start the application.
- Next, in the tab, set the number of seconds of delay before the function starts. The default is zero seconds.
- Click on and
- When the mouse-cursor turns to cross-hairs, place it inside the application window and left-click.
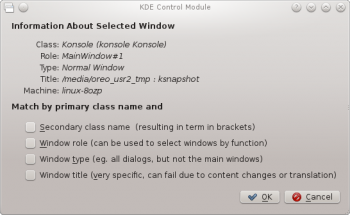
- A new window is presented with information about the selected window:
- Class
- Role
- Type
- Title
- Machine (hostname)
Click the button to back-fill the criteria.
By using a combination of the information, you can tailor whether a rule applies to an entire application (by Class) or a to a specific window Type within the Class - say a Toolbar.
Window Attributes
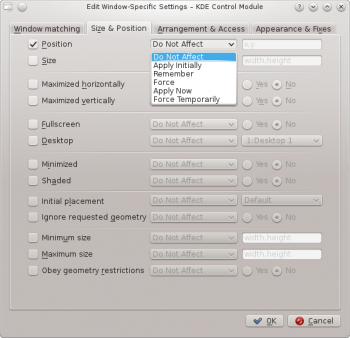
The attributes which can be set are grouped in three tabs:
Each attribute has additional settings which determine when they're applied and depending on the attribute, there may be an additional argument.
Attributes
Size & Position
- Position
- Position the window's upper left corner at the specified x,y coordinate.

Tip
- Size
- The width and height of the window.
- Maximized horizontally, Maximized vertically, Fullscreen
- These attributes are used to toggle the maximum horizontal/minimum horizontal/full-screen window attribute.
- Desktop
- Place the window on the designated (Virtual) Desktop Use 'All Desktops to place the window on all Virtual Desktops.
- Minimized, Shaded
- Toggle the Minimize and Shading window attribute. For example, a window can be started Minimized or if it is started Minimized, it can be forced to not.

Tip
- Initial placement
- Override the global window placement strategy.
- Ignore requested geometry
- <---- placeholder ...
- Minimum size
- Def
- Maximum size
- Def
- Obey geometry restrictions
- Def
Arrangement & Access
- Keep above
- Def
- Keep below
- Def
- Autogroup with identical
- Def
- Autogroup in foreground
- Def
- Autogruop by ID
- Def
- Tiling
- Def
- Skip taskbar
- Def
- Skip pager
- Def
- Skip switcher
- Def
- Shortcut
- Def
Appearance & Fixes
- Not titlebar and frame
- Def
- Active opacity
- Def
- Inactive opacity
- Def
- Moving/resizing
- Def
- Focus stealing prevention
- Def
- Accept focus
- Def
- Ignore global shortcuts
- Def
Disposition
- Do Not Affect
- Definition
- Apply Initially
- Definition
- Remember
- Def
- Force
- Def
- Apply Now
- Def
- Force Temporarily
- Def
Examples
Force a Window on a Desktop
Force a Window on all Desktops
Suppress a Window showing on Pager
Force a Window to the Top
Good for knotes
Multiple Rules per Application
e.g. Thunderbird on one desktop and composition window on any
