System Settings/Task Scheduler: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(Marked this version for translation) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<translate> | <translate> | ||
=== General Information === | === General Information === <!--T:1--> | ||
{|class="tablecenter vertical-centered" | {|class="tablecenter vertical-centered" | ||
|[[Image:Preferences-system.png|48px]] KCron is a tool for running applications in the background at regular intervals. It's a graphical interface to the Cron command. | |[[Image:Preferences-system.png|48px]] KCron is a tool for running applications in the background at regular intervals. It's a graphical interface to the Cron command. | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
|} | |} | ||
<!--T:2--> | |||
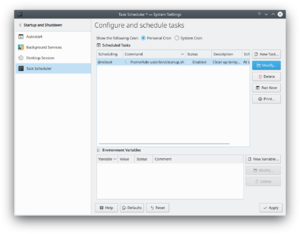
[[Image:Kcron-screenshot-de.png|thumb|300px|center|KCron in KDE SC 4]] | [[Image:Kcron-screenshot-de.png|thumb|300px|center|KCron in KDE SC 4]] | ||
=== Usage === | === Usage === <!--T:3--> | ||
<!--T:4--> | |||
First define what variables your application needs and their values, then select your application. When this is done you select at which times your application should be run and you're all set. | First define what variables your application needs and their values, then select your application. When this is done you select at which times your application should be run and you're all set. | ||
<!--T:5--> | |||
In{{KDE4}} | In{{KDE4}} | ||
In 4.4 '''KCron''' is a module which could be found in <menuchoice>system settings -> advanced -> system section -> task scheduler</menuchoice>. If it is not present, please check that you have the kdeadmin package installed. In KDE 4.5 you will find it in <menuchoice>systemsettings -> System Administration section -> Task Scheduler</menuchoice>. Some distros make kcron a separate package, so if it's not visible you should query your repository for it. | In 4.4 '''KCron''' is a module which could be found in <menuchoice>system settings -> advanced -> system section -> task scheduler</menuchoice>. If it is not present, please check that you have the kdeadmin package installed. In KDE 4.5 you will find it in <menuchoice>systemsettings -> System Administration section -> Task Scheduler</menuchoice>. Some distros make kcron a separate package, so if it's not visible you should query your repository for it. | ||
<!--T:6--> | |||
In{{KDE3}} | In{{KDE3}} | ||
KCron can be started using ALT+F2 or K-Menu. | KCron can be started using ALT+F2 or K-Menu. | ||
=== Hints === | === Hints === <!--T:7--> | ||
<!--T:8--> | |||
* All the files that are modified are located in the /etc/cron directory where there are numerous files to look at. | * All the files that are modified are located in the /etc/cron directory where there are numerous files to look at. | ||
<!--T:9--> | |||
* The command-line tool that allows you to have a look at the currently installed cron-jobs is <i>crontab -l</i> (that's the letter L). | * The command-line tool that allows you to have a look at the currently installed cron-jobs is <i>crontab -l</i> (that's the letter L). | ||
<!--T:10--> | |||
[[Category:System]] | [[Category:System]] | ||
[[Category:KDE3]] | [[Category:KDE3]] | ||
</translate> | </translate> | ||
Revision as of 12:52, 3 October 2010
General Information
Usage
First define what variables your application needs and their values, then select your application. When this is done you select at which times your application should be run and you're all set.
In
![]() In 4.4 KCron is a module which could be found in . If it is not present, please check that you have the kdeadmin package installed. In KDE 4.5 you will find it in . Some distros make kcron a separate package, so if it's not visible you should query your repository for it.
In 4.4 KCron is a module which could be found in . If it is not present, please check that you have the kdeadmin package installed. In KDE 4.5 you will find it in . Some distros make kcron a separate package, so if it's not visible you should query your repository for it.
In
![]() KCron can be started using ALT+F2 or K-Menu.
KCron can be started using ALT+F2 or K-Menu.
Hints
- All the files that are modified are located in the /etc/cron directory where there are numerous files to look at.
- The command-line tool that allows you to have a look at the currently installed cron-jobs is crontab -l (that's the letter L).
