Guies d'aprenentatge/Base de dades compartida
Base de dades compartida
Hi ha diverses aplicacions d'escriptori per a KDE que tenen a veure amb algun tipus de base de dades. Les més conegudes són probablement Amarok el reproductor de música, digiKam el gestor de fotos i Akonadi l'entorn d'informació personal. Per simplificar la instal·lació i limitar el seus requisits, cadascun d'aquests programes disposa d'una base de dades pròpia, en la majoria dels casos utilizant SQLite. Tenir moltes bases de dades separades crea una sobrecàrrega innecessària, i fa més difícil el crear una còpia de seguretat de totes les vostres dades.
Servidor de base de dades
La base de dades universalment suportada en aquests programes és MySQL, de manera que serà la que usarem. També és molt fàcil de configurar, ja sigui per la línia d'ordres o amb eines gràfiques.
Instal·lació
First, we have to install the mysql server. Linux users will probably want to install a package from their distribution, other can get it from their homepage. Instructions to start MySQL at boot are distribution-specific, but since MySQL is a popular package, they shouldn't be hard to find. During the installation, the installer will probably ask you for a root password. Choose a secure password for this and remember it, this account will not be used by the desktop applications but only for database administration.
Configuració
For the server configuration, this we will assume that your database server is not used over the network, contains no sensitive data, and that you trust your applications. If you plan to use this database for Akonadi data, it's best if you copy the configuration file from the Akonadi code repository, which can be downloaded at here. Make a copy of your existing /etc/mysql/my.cnf, then replace it with the downloaded file.
Crear les bases de dades
The first thing we have to do once MySQL is installed and running is add a separate database for each program. I generally name them after the programs that use them. This can be done with either GUI administration tools, but since we only have to do it once it's probably faster to write a few commands:
$ mysql -u root -p
At the password prompt, type in the root password set when installing MySQL. Now we can start creating databases. For example, to create a database named 'amarok', type in this command:
mysql> create database amarok;
Amarok
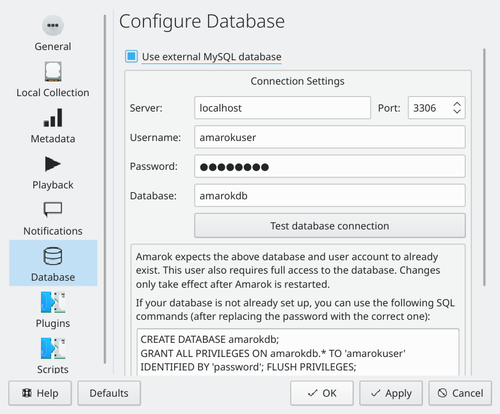
Amarok requires very little configuration, but it doesn't provide a way to migrate your old database. Go to and go to the tab.
Fill in localhost in the textfield, 3306 in , and amarok in .
digiKam
digiKam is somewhat special because it requires two databases: one for the images metadata, and one for thumbnails. Their names are not important, I chose to call them digikam and digikam_thumb:
mysql> create database digikam; mysql> create database digikam_thumb;
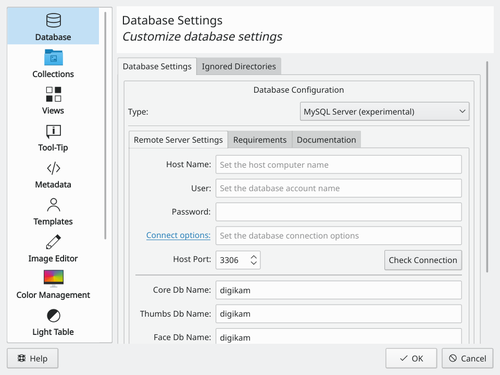
In digiKam, the process is very similar to that of Amarok. The settings are located in .
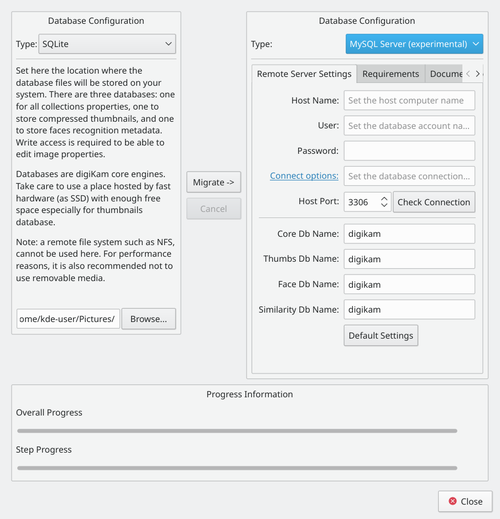
digiKam also comes with a handy database migration tool, available in . Fill in your previous database settings (you don't have to do anything if you haven't changed these options) on the left side and your new settings on the right side, then click .
Akonadi
First create a database for Akonadi:
mysql -u root -p create database akonadi;
Akonadi is not supposed to be a user-facing tool, so there is no configuration GUI for it. However, you can edit
~/.config/akonadi/akonadiserverrc to have these contents:
[%General] Driver=QMYSQL [QMYSQL] Name=akonadi Host=localhost StartServer=false Options= ServerPath=/usr/bin/mysqld
Save the file, then log out and log in back again.


