Systemovervågning
Introduktion
Systemovervågning minder om Microsoft Windows' Task Manager, Apple Mac OS X's Activity Monitor og Gnomes System Monitor. Den dukker op, når du taster Ctrl + Esc eller klikker på Systemovervågnings ikon,![]() , til venstre i et KRunner-vindue ((Alt + F2)).
, til venstre i et KRunner-vindue ((Alt + F2)).
Den viser en liste med de processer, som kører på maskinen sammen med deres forbrug af CPU og hukommelse samt anden information.
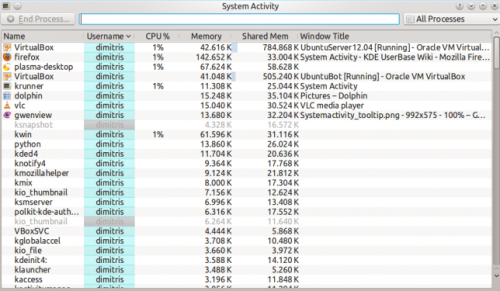
Generelle tips
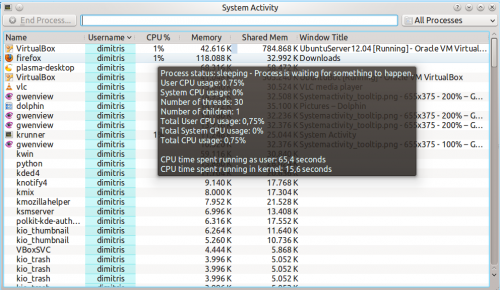
Næsten alle elementer i vinduet viser et tooltip, som giver mere detaljeret information, når du lader musen svæve over det og når du klikker på ![]() ikonet, så aktiveres "Hvad Er Det"-funktionen, som forklarer hvad informationen betyder.
ikonet, så aktiveres "Hvad Er Det"-funktionen, som forklarer hvad informationen betyder.
Hvis du fx lader musen svæve over CPU-forbruget for en proces, så ser du forskellige andre informationer herunder den samlede tid, som processen har kørt.
Hvorfor kører mit system langsomt nu?
A system can be running unusually slow because a process (program) is demanding all of the computer's processing power (CPU usage) or is using all of the computer's memory.
By default, processes owned by the current user that are using a lot of CPU or memory are near the top. This means that any misbehaving programs should be near the top and easily visible. For example:
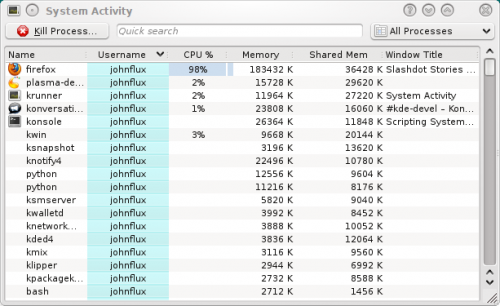
In this example, Firefox has stopped responding and is using 99% of CPU.
To end the process that is misbehaving, click on the process to select it and press the button. This will send a polite request to the program, asking it to close.
I can't kill it - it just won't die!
Thankfully it's fairly rare, but just occasionally you may meet this. If the process is misbehaving it may ignore your request to end, so we may need to force the program to end immediately. Doing this may result in any documents etc that the program had opened but not saved. To do this, right click on the process and choose then choose .
Sometimes even this will not kill the process, or the option will not be given. This can happen, for example, in vuze with certain kernels. If the process or one of its threads gets caught in a kernel bug then it can end up being stuck trying to execute a kernel operation and being completely unkillable. Often there is no solution to this other than rebooting the machine.
Zombie processes
Processes which are in a Zombie state are already dead, and so cannot be killed. The system keeps them around until their parent process notices, which is usually a very short amount of time. Seeing a Zombie process usually indicates that the parent process has stopped responding.
Targeting a window to kill
If you want to kill a particular window that has frozen up, simply press Ctrl + Alt + Esc at any time. The mouse cursor should turn into an image of a skull and cross bones. Now click the window that you want to kill. Note that this will kill the application immediately, and you may lose any unsaved data.
The Memory column shows approximately the amount of memory (RAM) that the process is using by itself, privately. The Shared Memory column is approximately the memory that is, or could be, shared with other programs. For example, the KDE libraries are used by all KDE programs and so are loaded into memory only once.
From KDE SC 4.4, you can right-click on a process and view the for the process to get more accurate readings.
Technical Information
The "Memory" column shows the value of VmRSS - Shared, and so is generally lower than the values shown by top etc. This does not include memory backed I/O pages, and does not include memory used by the x server to store any pixmaps used by the application. This value is often called the Unique RSS size, or URSS. This approximates the value shown as Private memory usage in the .
The Shared memory is the same as the SHR column in top and can be somewhat inaccurate. This approximates the value shown as Shared memory usage in the .
Specifically the process list parses /proc/pid/stat whereas the dialog parses /proc/pid/smaps.
How do I view more Detailed Memory Information about a process?
From KDE SC 4.4 you will be able to select a process in the table, right click on the process, and choose , and get something like:
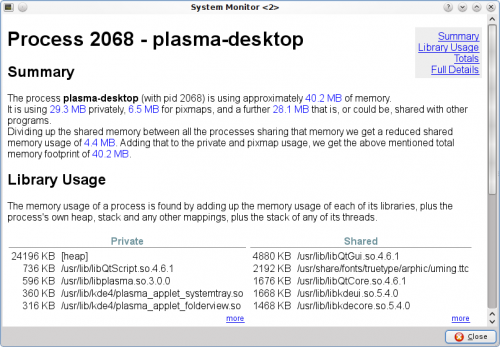
Why do values in Detailed Memory Information not match the process list?
The process list in System Activity is using an approximation to gather the values. The gives more accurate values.
Why is the "Xorg" process using so much memory?
This is the process that displays all the other applications. Its memory usage includes all the memory used on the video card to store all the pixmaps (images) from applications.
In general you do not need to worry about the memory usage of Xorg.
How do I see the PID of a process?
If you want to see the PID of a single process, hover the mouse cursor over the name of the process. The PID will be shown in the tooltip.
If you want to see the PID of all the processes, right click on any column heading and you will see the menu:
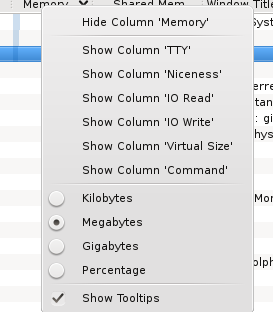
Choose .
Why are some processes grayed out?
For example the process xclock:
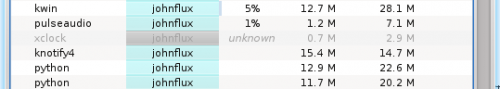
This means that the process has already died. It is shown as a disabled
process just for convenience to make it easier to see processes that are quit.
The values for the CPU usage, Memory usage, etc are just the values from when the process was last seen alive. A process that has ended does not take up any resources (it uses no CPU, memory etc).
What are all of these processes owned by root and taking up no memory?
These are kernel threads. They exist only inside the kernel, and exist to allow the kernel to perform multiple tasks in parallel.
They are shown because occasionally they can be a cause of heavy CPU usage. For example, under a heavy load, and with bad drivers, a network card can produce a huge number of interrupts, resulting in a high CPU usage in the ksoftirqd kernel thread.
Likewise, a high CPU usage in kjournald can indicate that DMA transfer is not enabled on the hard disk.
Why do I have so many processes?
A normal average-user system has around 150 to 200 processes with strange sounding names. It would be nice to setup a wiki page giving a short description of each of these processes, but so far nobody has done this. :-)
Why is OpenOffice.org not showing up as a graphical program?
Before version 3.3, OpenOffice.org did not correctly implement the window standards. Specifically, their windows did not set _NET_WM_PID to link the windows to the process. This is now fixed in OpenOffice.org 3.3.
