Amarok/Manual/ConfiguringAmarok

Configuring Amarok
On first start, some basic configuration is done, see also Quick Start Guide: Getting Started. But there is more under the hood. To access the Configuration Menu, you go to and will be presented with the following dialog:
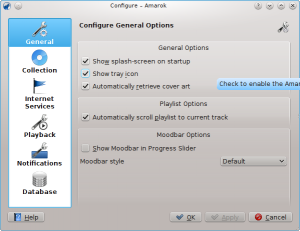
General
In the screenshot above you can see some General Options you can set. Depending on the distribution, the default settings can vary, sometimes the Splash Screen is disabled for example. When hovering over the options with the mouse pointer, a tooltip will show to explain the individual settings.
This section allows you to configure the following options:
| Option | Tooltip |
| Show splash-screen on startup | Check to enable the splash screen on Amarok startup |
| Show tray icon | Check to enable the Amarok system tray icon |
| Automatically retrieve cover art | Check to enable the automatic retrieval of cover art from the internet |
| Automatically scroll playlist to current track | Check to enable playlist scrolling to the currently played track |
| Show Moodbar in progress slider | The Moodbar makes it possible to navigate in your music visually. Please note that this feature requires the external "Moodbar Generator" tool |
| Moodbar style | Choose the mood display style |
When you enable the Moodbar, be aware of the following requirements: the moodbar will only display if your tracks have been tagged with moods. To know more about the Advanced Feature Moodbar, please refer to this section: Advanced Features -> Moodbar
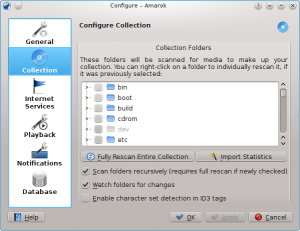
Collection
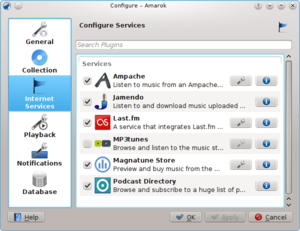
Internet Services
Playback
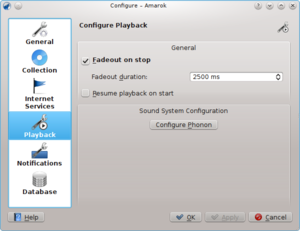
In the above Playback section you can configure the playback options, as well as the KDE multimedia framework called Phonon.
| Option | Tooltip |
| Fadeout on stop | |
| Fadeout duration | |
| Resume playback on start | If checked, Amarok will resume playback where you left it the last session -- just like a tape-player |
Configuring Phonon
KDE versions 2 and 3 uses aRts as their multimedia framework. Over the lifespan of these releases aRts fell behind newer frameworks such as Xine and GStreamer and is by now unmaintained. Learning from these mistakes, KDE implemented Phonon for KDE 4.
Phonon was created to allow KDE 4 to be independent of any single multimedia framework such as GStreamer or Xine and to provide a stable API for KDE 4's lifetime. As an added bonus, it simplifies development by providing a simple API that can work across different platforms such as Windwows and OS X.
The result of all this for you, the user, is that you get to choose the multimedia framework that works best for you. For Linux users the currently recommended choice is Xine, but this may or may not hold true for you.
Another result is that playback problems in Amarok are typically not Amarok issues, but rather Phonon issues. It is for that reason that this page exist.
Selecting an output device
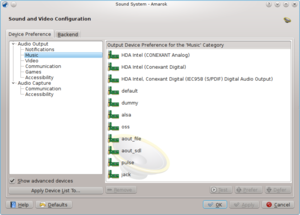
Depending on your OS and distribution, you may need to use ALSA, OSS, PulseAudio, or something else as your default playback device. Find one that works for you with the "Test" button and apply to all types of output. If you would like different types of output to go with different devices, this is certainly possible as well.
Selecting a multimedia backend
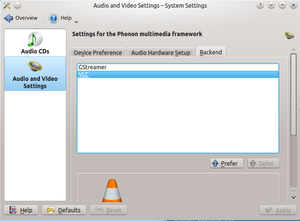
Depending on your OS you may see options such as Xine, GStreamer, VLC, or DS9 (Windows only) here. The recommended one for Linux users is Xine. VLC is recommended for Windows users, but is experimental like the rest of KDE for Windows.
If you don't see Xine or the particular back-end you want here you may need to install the package for it. For most distributions the package for Xine, for example, would be phonon-backend-xine. If you need more detailed instructions you should see your distro's section on the download page.
For information on playing MP3's see the MP3 page.
Notifications
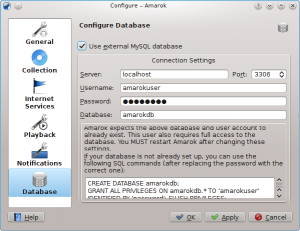
Database