Amarok/Manual/Organization/Collection/RemoteCollections
Introduction
Amarok allows you to store information like bookmarks, lyrics, playlists and statistics in an external database.
Configure Server
Install MySQL-Server
First you need to install an MySQL-Server, either on the local or another computer on the same network. On Debian-based distributions like Ubuntu you can use sudo apt-get install mysql-server to install it. You will be asked to specify a password for the root-account for the database.
Configure Database
Connect to the local database using mysql -u root -p mysql. Then you will get the mysql> prompt.
Create a new user amarokuser with the password amarokpass using the CREATE USER 'amarokuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'amarokpass'; command. Amarok needs its own database, which is created with CREATE DATABASE amarokdb;. Give the new user access to the database by entering the GRANT ALL ON amarokdb.* TO 'amarokuser'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'amarokpass'; command, where % is a wildcard to allow all hosts to connect to the database. Now use the FLUSH PRIVILEGES; statement to reload various internal caches used by MySQL. Finally exit closes the MySQL-prompt.
By default the server can only be accessed by the local host. To change this you need to edit the file /etc/mysql/my.cnf and adjust the address near bind-address to the one your server listens on the network. 0.0.0.0 listens on all interfaces. After that you need to restart the server using sudo service mysql restart.
Configure Client
Open the configuration dialog by clicking . Enable the checkbox and enter the user data.
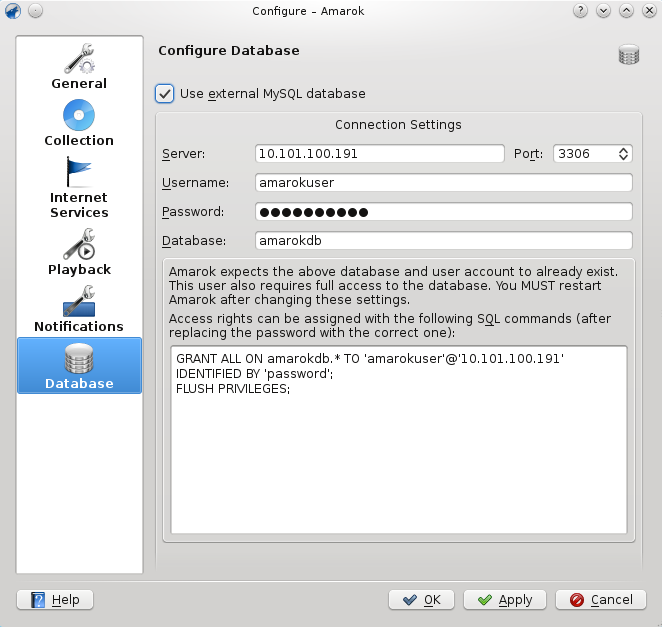
You need to restart Amarok so that the changes take effect.
