KAlgebra/Probabilities: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "=== Introduction === Let's say we have 5 dices and we want to gamble with them. === Theory behind game === First we have to analyze one die: The probability to get a number ...") |
(correct links) |
||
| (45 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<languages /> | |||
<translate> | |||
<!--T:1--> | |||
This page shows some uses of '''KAlgebra''' in probabilities problem | |||
== Introduction == <!--T:2--> | |||
<!--T:3--> | |||
Let's say we have 5 dices and we want to gamble with them. | Let's say we have 5 dices and we want to gamble with them. | ||
<!--T:4--> | |||
[[Image:25849-IMG_0837_1600.JPG|200px|right]] | |||
== Theory behind game == <!--T:5--> | |||
<!--T:6--> | |||
First we have to analyze one die: | First we have to analyze one die: | ||
<!--T:7--> | |||
The probability to get a number on a dice is 1/6 or 16,667% because the total numbers of events is 6 and the die is equiprobal. | The probability to get a number on a dice is 1/6 or 16,667% because the total numbers of events is 6 and the die is equiprobal. | ||
The probability to get each number is on the | <!--T:8--> | ||
The probability to get each number is on the right | |||
<!--T:9--> | |||
{{Input| | {{Input| | ||
1 16.667% | 1 16.667% | ||
| Line 21: | Line 35: | ||
When we launch 2 dices probabilities change, so we report them: | When we launch 2 dices probabilities change, so we report them: | ||
<!--T:10--> | |||
{{Input| | {{Input| | ||
2 2.778% | 2 2.778% | ||
| Line 35: | Line 50: | ||
}} | }} | ||
<!--T:11--> | |||
Why is the probability for each number so different respect to first one, you may ask, the solution is very simple. Let's take '4' and make all the combinations of 2 numbers that summed gives 4: | Why is the probability for each number so different respect to first one, you may ask, the solution is very simple. Let's take '4' and make all the combinations of 2 numbers that summed gives 4: | ||
1+3 = 4 | <!--T:12--> | ||
1+3 = 4 | |||
3+1 = 4 | 3+1 = 4 | ||
2+2 = 4 | 2+2 = 4 | ||
<!--T:13--> | |||
So we have to sum the probability of these numbers to get the total probability of 4. Let's test it: | So we have to sum the probability of these numbers to get the total probability of 4. Let's test it: | ||
Prob(1,3) + Prob(3,1) + Prob(2,2) = 1/6 * 1/6 + 1/6 * 1/6 + 1/6 * 1/6 = 0.08333 = 8,333% | <!--T:14--> | ||
Prob(1,3) + Prob(3,1) + Prob(2,2) = 1/6 * 1/6 + 1/6 * 1/6 + 1/6 * 1/6 = 0.08333 = 8,333% | |||
<!--T:15--> | |||
So if we have 5 dice, we should get for each resulting number the 5 numbers on dice that summed up give us it. The way to get the probabilities of each number with more dices is equal. | So if we have 5 dice, we should get for each resulting number the 5 numbers on dice that summed up give us it. The way to get the probabilities of each number with more dices is equal. | ||
== The probability problem == <!--T:16--> | |||
<!--T:17--> | |||
Now we mind at a problem, if we roll our 5 dice and we want 3 '6', what is the probability to get them? | Now we mind at a problem, if we roll our 5 dice and we want 3 '6', what is the probability to get them? | ||
<!--T:18--> | |||
ok, the problem is: probability on first dice * probability on second dice * probability on third dice * negative probability on fourth * negative probability on fifth | ok, the problem is: probability on first dice * probability on second dice * probability on third dice * negative probability on fourth * negative probability on fifth | ||
So for instance the dice can be: 6 6 6 2 3, but they can also be 5 6 6 6 1, so we have to introduce a binomial | <!--T:19--> | ||
To have | So for instance the dice can be: '''6 6 6 2 3''', but they can also be '''5 6 6 6 1''', so we have to introduce a binomial coefficient to count all this cases. | ||
To have the binomial coefficient of '''N''' numbers on '''M''' position the formula for '''KAlgebra''' is: | |||
{{Input|1=factorial(N) / (factorial(M) * factorial(N-M))}} | {{Input|1=factorial(N) / (factorial(M) * factorial(N-M))}} | ||
This is the combinatorial coefficient, which we can define like this: | |||
{{Input|1=comb(N,M)}} | <!--T:20--> | ||
{{Input|1=comb:=(N,M)->factorial(N) / (factorial(M) * factorial(N-M))}} | |||
So the binomial | <!--T:21--> | ||
So the binomial coefficient of 3 numbers on 5 position is: | |||
<!--T:22--> | |||
{{Input|1=comb(5,3)}} | {{Input|1=comb(5,3)}} | ||
{{Output|1== 10}} | {{Output|1== 10}} | ||
<!--T:23--> | |||
so at last our function will be: | so at last our function will be: | ||
<!--T:24--> | |||
{{Input|1=(comb(5, 3)*(1/6)*(1/6)*(1/6)*(5/6)*(5/6))}} | {{Input|1=(comb(5, 3)*(1/6)*(1/6)*(1/6)*(5/6)*(5/6))}} | ||
{{Output|1== 0. | {{Output|1== 0.0321502}} | ||
<!--T:25--> | |||
We can now define a simple function to get the result: | We can now define a simple function to get the result: | ||
{{Input| | <!--T:26--> | ||
{{Input|1=binomial:=(b, p, k)->(comb(b, k)*p^k)*(1-p)^(b-k)}} | |||
}} | |||
<!--T:27--> | |||
So now: | So now: | ||
{{Input|1= | <!--T:28--> | ||
{{Input|1=binomial(5, 1/6,3)}} | |||
{{Output|1== 0.0321502}} | {{Output|1== 0.0321502}} | ||
<!--T:29--> | |||
It's the probability on 5 extraction to get 3 identical number where the probability of each card is 1/6 and the negative probability is 5/6 | It's the probability on 5 extraction to get 3 identical number where the probability of each card is 1/6 and the negative probability is 5/6 | ||
<!--T:30--> | |||
We can notice that the sum of probabilities is 1: | We can notice that the sum of probabilities is 1: | ||
{{Input|1=sum( | <!--T:31--> | ||
{{Input|1=sum(binomial(5,1/6,t):t=0..5)}} | |||
{{Output|1== 1}} | {{Output|1== 1}} | ||
We can think that the probability progress until the maximum value and then it decrease | <!--T:32--> | ||
We can think that the probability progress until the maximum value and then it decrease constantly as it has progressed. So we can see that the distribution of numbers among the extraction is like a bell, this kind of distribution is called a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binomial_distribution binomial distribution]. | |||
<!--T:33--> | |||
So now we understand that the game is non balanced, there are probabilities better than other so who choose the best can win easily. | So now we understand that the game is non balanced, there are probabilities better than other so who choose the best can win easily. | ||
<!--T:34--> | |||
The only way to have a fair game is to gambling with only one die because each face has 1/6 of probability. Another type of equiprobal chances are the launch of a coin where each face is 1/2 of probability. | The only way to have a fair game is to gambling with only one die because each face has 1/6 of probability. Another type of equiprobal chances are the launch of a coin where each face is 1/2 of probability. | ||
A simple way where a player can win is to improve the probability on a face so it will be unbalanced, for | <!--T:35--> | ||
A simple way where a player can win is to improve the probability on a face so it will be unbalanced, for instance the bank in a game can put a small load on the face with '6' so the probabilities change and the dice now became: | |||
<!--T:36--> | |||
{{Input| | {{Input| | ||
0.15 1 | 0.15 1 | ||
| Line 107: | Line 146: | ||
}} | }} | ||
<!--T:37--> | |||
So now if we roll the 5 dices with this probability and we want 3 '6' to win the total probability is: | So now if we roll the 5 dices with this probability and we want 3 '6' to win the total probability is: | ||
{{Input|1=probability(5, 3, 6, 2, 4)}} | <!--T:38--> | ||
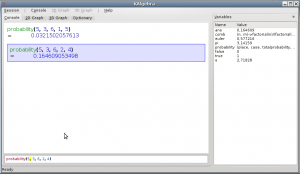
{{Output|1== | {{Input|1=binomial(5,0.25,3)}} | ||
{{Output|1= = 0.087890625}} | |||
<!--T:39--> | |||
[[Image:Kalgebra-dice.png|300px|right|Snapshot of '''KAlgebra''' window doing calculations about probabilities]] | |||
=== Real World Example === <!--T:40--> | |||
<!--T:41--> | |||
There are two person, the bank and the player. | |||
Let's say they have 5 dices and the entrance fee for player is 1$. We can create a game like this: | |||
<!--T:42--> | |||
0 to 1 times dice with '6': player loses 1$ with the fee | |||
<!--T:43--> | |||
2 to 3 times dice with '6': player win 1$ with the fee | |||
<!--T:44--> | |||
4 times dice with '6': player win 175$ with the fee | |||
<!--T:45--> | |||
5 times dice with '6': player win 375$ with the fee | |||
<!--T:46--> | |||
{|class="tablecenter" style="border: 1px solid grey;" | |||
! k times '6' | |||
! win or loose | |||
|- | |||
| 0 | |||
| -1$ | |||
|- | |||
| 1 | |||
| -1$ | |||
|- | |||
| 2 | |||
| 1$ | |||
|- | |||
| 3 | |||
| 1$ | |||
|- | |||
| 4 | |||
| 175$ | |||
|- | |||
| 5 | |||
| 375$ | |||
|} | |||
<!--T:47--> | |||
Let's calculate the probability: | |||
<!--T:48--> | |||
Probability for player: | |||
<!--T:49--> | |||
The player can win only with 2-3 times '''6''', 4 times '''6''' or 5 times '''6''', so if we want to process the probability with '''KAlgebra''' it will be: | |||
<!--T:50--> | |||
{{Input| | |||
binomial(5,1/6,2)+binomial(5,1/6,3)+binomial(5,1/6,4)+binomial(5,1/6,5) | |||
}} | |||
{{Output| | |||
1== 0.196244855967 | |||
}} | |||
<!--T:51--> | |||
Probability for bank: | |||
<!--T:52--> | |||
The bank can win only with 0-1 times '''6''', so if we want to process the probability with '''KAlgebra''' it will be: | |||
<!--T:53--> | |||
{{Input| | |||
binomial(5,1/6,0)+binomial(5,1/6,1) | |||
}} | |||
{{Output| | |||
1== 0.803755144033 | |||
}} | |||
<!--T:54--> | |||
We now want to see if player and bank are balanced, | |||
We create a function win(x), that create a correspondence between values and prizes: | |||
<!--T:55--> | |||
{{Input|1= | |||
win:=x->piecewise { x=0 ? -1, x=1 ? -1, x=2 ? 1, x=3 ? 1, x=4 ? 175, x=5 ? 375, ? 0 } | |||
}} | |||
<!--T:56--> | |||
Let's verify the expression with '''KAlgebra''': | |||
<!--T:57--> | |||
{{Input| | |||
1=sum(win(x)*binomial(5,1/6,x): x=0..5) | |||
}} | |||
{{Output| | |||
1== -2.01227923213e-16 | |||
}} | |||
<!--T:58--> | |||
The result should be 0, but because of the internal representation of numbers in the computer the result is not exact. | |||
<!--T:59--> | |||
As we can see the problem is equilibrated and player and bank will not win or lose anything for an infinite number of games. | |||
<!--T:60--> | |||
[[Category:Education]] | |||
</translate> | |||
Latest revision as of 09:34, 7 October 2022
This page shows some uses of KAlgebra in probabilities problem
Introduction
Let's say we have 5 dices and we want to gamble with them.

Theory behind game
First we have to analyze one die:
The probability to get a number on a dice is 1/6 or 16,667% because the total numbers of events is 6 and the die is equiprobal.
The probability to get each number is on the right
1 16.667%
2 16.667%
3 16.667%
4 16.667%
5 16.667%
6 16.667%
When we launch 2 dices probabilities change, so we report them:
2 2.778%
3 5.556%
4 8.333%
5 11.111%
6 13.889%
7 16.667%
8 13.889%
9 11.111%
10 8.333%
11 5.556%
12 2.778%
Why is the probability for each number so different respect to first one, you may ask, the solution is very simple. Let's take '4' and make all the combinations of 2 numbers that summed gives 4:
1+3 = 4 3+1 = 4 2+2 = 4
So we have to sum the probability of these numbers to get the total probability of 4. Let's test it:
Prob(1,3) + Prob(3,1) + Prob(2,2) = 1/6 * 1/6 + 1/6 * 1/6 + 1/6 * 1/6 = 0.08333 = 8,333%
So if we have 5 dice, we should get for each resulting number the 5 numbers on dice that summed up give us it. The way to get the probabilities of each number with more dices is equal.
The probability problem
Now we mind at a problem, if we roll our 5 dice and we want 3 '6', what is the probability to get them?
ok, the problem is: probability on first dice * probability on second dice * probability on third dice * negative probability on fourth * negative probability on fifth
So for instance the dice can be: 6 6 6 2 3, but they can also be 5 6 6 6 1, so we have to introduce a binomial coefficient to count all this cases. To have the binomial coefficient of N numbers on M position the formula for KAlgebra is:
factorial(N) / (factorial(M) * factorial(N-M))
This is the combinatorial coefficient, which we can define like this:
comb:=(N,M)->factorial(N) / (factorial(M) * factorial(N-M))
So the binomial coefficient of 3 numbers on 5 position is:
comb(5,3)
= 10
so at last our function will be:
(comb(5, 3)*(1/6)*(1/6)*(1/6)*(5/6)*(5/6))
= 0.0321502
We can now define a simple function to get the result:
binomial:=(b, p, k)->(comb(b, k)*p^k)*(1-p)^(b-k)
So now:
binomial(5, 1/6,3)
= 0.0321502
It's the probability on 5 extraction to get 3 identical number where the probability of each card is 1/6 and the negative probability is 5/6
We can notice that the sum of probabilities is 1:
sum(binomial(5,1/6,t):t=0..5)
= 1
We can think that the probability progress until the maximum value and then it decrease constantly as it has progressed. So we can see that the distribution of numbers among the extraction is like a bell, this kind of distribution is called a binomial distribution.
So now we understand that the game is non balanced, there are probabilities better than other so who choose the best can win easily.
The only way to have a fair game is to gambling with only one die because each face has 1/6 of probability. Another type of equiprobal chances are the launch of a coin where each face is 1/2 of probability.
A simple way where a player can win is to improve the probability on a face so it will be unbalanced, for instance the bank in a game can put a small load on the face with '6' so the probabilities change and the dice now became:
0.15 1 0.15 2 0.15 3 0.15 4 0.15 5 0.25 6
So now if we roll the 5 dices with this probability and we want 3 '6' to win the total probability is:
binomial(5,0.25,3)
= 0.087890625
Real World Example
There are two person, the bank and the player. Let's say they have 5 dices and the entrance fee for player is 1$. We can create a game like this:
0 to 1 times dice with '6': player loses 1$ with the fee
2 to 3 times dice with '6': player win 1$ with the fee
4 times dice with '6': player win 175$ with the fee
5 times dice with '6': player win 375$ with the fee
| k times '6' | win or loose |
|---|---|
| 0 | -1$ |
| 1 | -1$ |
| 2 | 1$ |
| 3 | 1$ |
| 4 | 175$ |
| 5 | 375$ |
Let's calculate the probability:
Probability for player:
The player can win only with 2-3 times 6, 4 times 6 or 5 times 6, so if we want to process the probability with KAlgebra it will be:
binomial(5,1/6,2)+binomial(5,1/6,3)+binomial(5,1/6,4)+binomial(5,1/6,5)
= 0.196244855967
Probability for bank:
The bank can win only with 0-1 times 6, so if we want to process the probability with KAlgebra it will be:
binomial(5,1/6,0)+binomial(5,1/6,1)
= 0.803755144033
We now want to see if player and bank are balanced, We create a function win(x), that create a correspondence between values and prizes:
win:=x->piecewise { x=0 ? -1, x=1 ? -1, x=2 ? 1, x=3 ? 1, x=4 ? 175, x=5 ? 375, ? 0 }
Let's verify the expression with KAlgebra:
sum(win(x)*binomial(5,1/6,x): x=0..5)
= -2.01227923213e-16
The result should be 0, but because of the internal representation of numbers in the computer the result is not exact.
As we can see the problem is equilibrated and player and bank will not win or lose anything for an infinite number of games.
