KWin Rules: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (101 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<languages /> | |||
<translate> | |||
==Overview== <!--T:1--> | |||
<!--T:2--> | |||
'''KWin''' allows the end-user to define rules to alter an application's window attributes. | |||
<!--T:3--> | |||
For example, when an application is started, it can be forced to always run on ''Virtual Desktop 2''. Or a defect in an application can be worked-around to force the window above others. | |||
<!--T:4--> | |||
Step-by-step [[Special:myLanguage/KWin_Rules_Examples|examples]] are provided along with detailed information on using the [[Special:myLanguage/KWin_Rules#KWin_Rule_Editor|'''KWin''' Rule Editor]] to specify [[Special:myLanguage/KWin_Rules_Window_Matching|Window Matching]] and [[Special:myLanguage/KWin_Rules_Window_Attributes|Window Attributes]]. | |||
</translate><span id="Examples_and_Application_Workaround"></span><translate> | |||
==Examples and Application Workaround== <!--T:5--> | |||
<!--T:6--> | |||
To see what's possible, detailed [[Special:myLanguage/KWin_Rules_Examples|examples]] are provided which can also be used to model your own rules. | |||
[[ | <!--T:7--> | ||
A special page is dedicated to address [[Special:myLanguage/KWin_Rules_Application_Workarounds|Application Workaround]]. | |||
</translate><span id="KWin_Rule_Editor"></span><translate> | |||
==KWin Rule Editor== <!--T:8--> | |||
</translate><span id="Invoking_the_KWin_Rule_Editor"></span><translate> | |||
=== | ===Invoking the KWin Rule Editor=== <!--T:9--> | ||
<!--T:10--> | |||
[[Image:kwin-rules-ordering.png|350px|center]] | |||
KWin | <!--T:11--> | ||
There are several ways to invoke the '''KWin''' Rule Editor. Below are two: | |||
<!--T:12--> | |||
* Right-click on the title-bar of any window, choose <menuchoice>More Actions</menuchoice>, <menuchoice>Configure Special Window Settings...</menuchoice> or | |||
<!--T:13--> | |||
* <menuchoice>System Settings -> Window Behavior -> Window Rules</menuchoice> | |||
The | <!--T:14--> | ||
The main window is used to: | |||
<!--T:15--> | |||
* Affect rules with <menuchoice>New...</menuchoice>, <menuchoice>Modify...</menuchoice> and <menuchoice>Delete</menuchoice> | |||
<!--T:16--> | |||
* Share rules with others via <menuchoice>Import</menuchoice> and <menuchoice>Export</menuchoice> | |||
<!--T:17--> | |||
* Ensure desired [[Special:myLanguage/KWin_Rules#Rule_Evaluation|rule evaluation]] using <menuchoice>Move Up</menuchoice> and <menuchoice>Move Down</menuchoice> | |||
</translate><span id="Rule_Evaluation"></span><translate> | |||
====Rule Evaluation==== <!--T:18--> | |||
<!--T:19--> | |||
When an application starts (or the rules are modified), '''KWin''' evaluates the rules from the top of the list to the bottom. For all rules which match a window, the collective set of attributes are applied to the window, then the window is displayed. | |||
: | <!--T:20--> | ||
Should two or more matching rules enable the same attribute, the setting in the ''first'' rule in the list is used. | |||
<!--T:21--> | |||
{{Tip|You can tailor children windows for the application by placing the more restrictive rules first - see the [[Special:myLanguage/KWin_Rules_Examples#Application_on_all_Desktops_and_Handle_One_Child_Window_Uniquely|Kopete and Kopete Chat Window]] example.}} | |||
= | </translate><span id="Rule_Editor"></span><translate> | ||
===Rule Editor=== <!--T:22--> | |||
<!--T:23--> | |||
[[Image:kwin-rule-editor.png|350px|center]] | |||
<!--T:24--> | |||
The editor is composed of four tabs: | |||
<!--T:25--> | |||
# <menuchoice>Window matching</menuchoice></translate> | |||
<translate> | |||
<!--T:26--> | |||
# <menuchoice>Size & Position</menuchoice></translate> | |||
<translate> | |||
# <menuchoice>Size & Position</menuchoice> | <!--T:27--> | ||
# <menuchoice>Arrangement & Access</menuchoice> | # <menuchoice>Arrangement & Access</menuchoice></translate> | ||
<translate> | |||
<!--T:28--> | |||
# <menuchoice>Appearance & Fixes</menuchoice> | # <menuchoice>Appearance & Fixes</menuchoice> | ||
<!--T:29--> | |||
As the name implies, <menuchoice>Window matching</menuchoice> is used to specify criteria to match one or more windows. The other three tabs are used to alter the attributes of the matching windows. | |||
<!--T:30--> | |||
{{Tip|Panels can also be affected.}} | |||
= | </translate><span id="Window_Matching"></span><translate> | ||
=== | ====Window Matching==== <!--T:31--> | ||
<!--T:32--> | |||
Each window rule has user specified [[Special:myLanguage/KWin_Rules_Window_Matching|Window Matching]] criteria. '''KWin''' uses the criteria to determine whether the rule is applicable for an application. | |||
= | </translate><span id="Window_Attributes"></span><translate> | ||
====Window Attributes==== <!--T:33--> | |||
<!--T:34--> | |||
Along with Window Matching criteria, each window rule has a set of [[Special:myLanguage/KWin_Rules_Window_Attributes|Window Attributes]]. The attributes override the corresponding application's settings and are applied before the window is displayed by '''KWin'''. | |||
<!--T:35--> | |||
[[Category:Desktop]] | |||
[[Category:Tutorials]] | |||
</translate> | |||
Latest revision as of 22:44, 22 January 2021
Overview
KWin allows the end-user to define rules to alter an application's window attributes.
For example, when an application is started, it can be forced to always run on Virtual Desktop 2. Or a defect in an application can be worked-around to force the window above others.
Step-by-step examples are provided along with detailed information on using the KWin Rule Editor to specify Window Matching and Window Attributes.
Examples and Application Workaround
To see what's possible, detailed examples are provided which can also be used to model your own rules.
A special page is dedicated to address Application Workaround.
KWin Rule Editor
Invoking the KWin Rule Editor
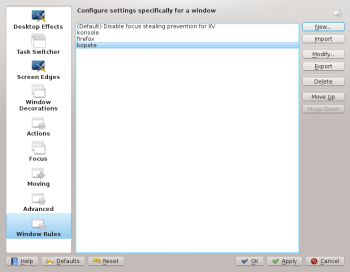
There are several ways to invoke the KWin Rule Editor. Below are two:
- Right-click on the title-bar of any window, choose , or
The main window is used to:
- Affect rules with , and
- Share rules with others via and
- Ensure desired rule evaluation using and
Rule Evaluation
When an application starts (or the rules are modified), KWin evaluates the rules from the top of the list to the bottom. For all rules which match a window, the collective set of attributes are applied to the window, then the window is displayed.
Should two or more matching rules enable the same attribute, the setting in the first rule in the list is used.
Rule Editor
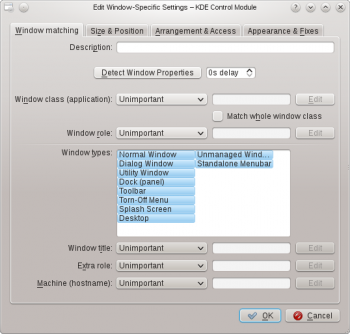
The editor is composed of four tabs:
As the name implies, is used to specify criteria to match one or more windows. The other three tabs are used to alter the attributes of the matching windows.
Window Matching
Each window rule has user specified Window Matching criteria. KWin uses the criteria to determine whether the rule is applicable for an application.
Window Attributes
Along with Window Matching criteria, each window rule has a set of Window Attributes. The attributes override the corresponding application's settings and are applied before the window is displayed by KWin.

